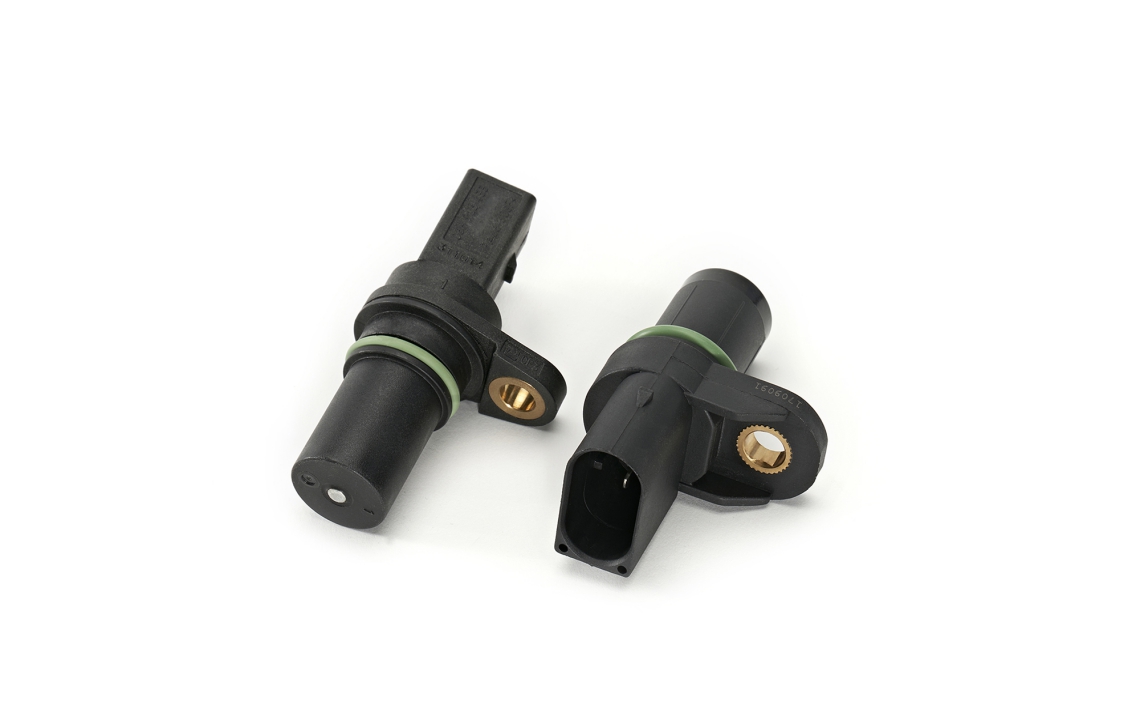
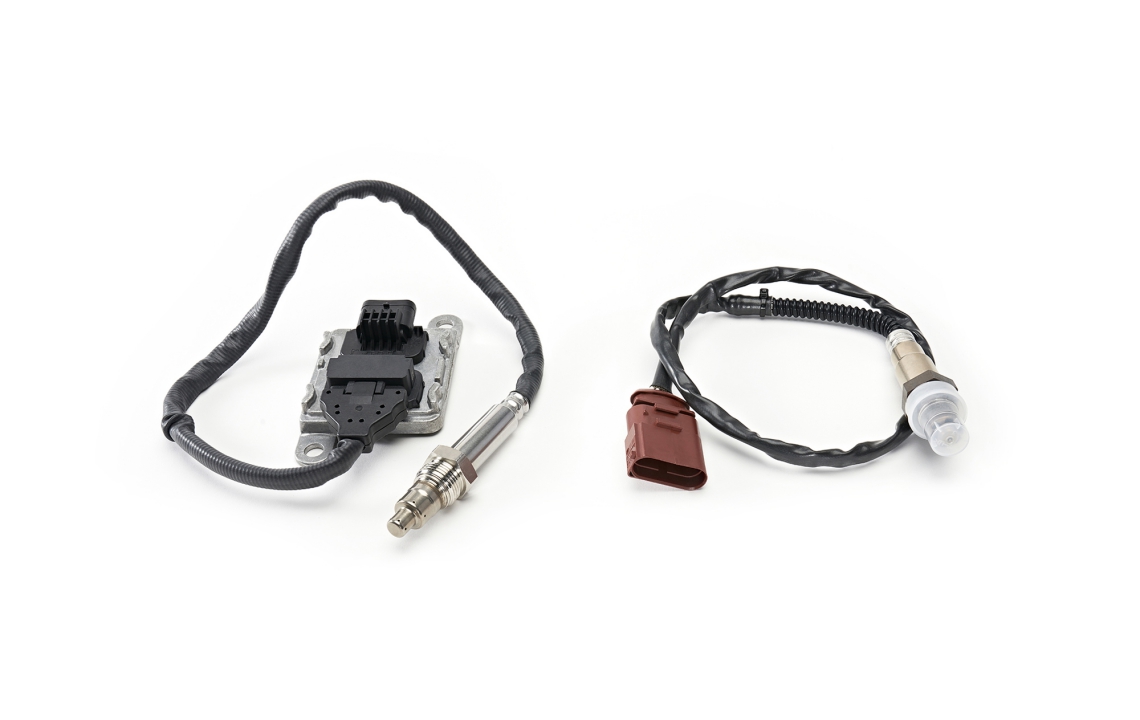
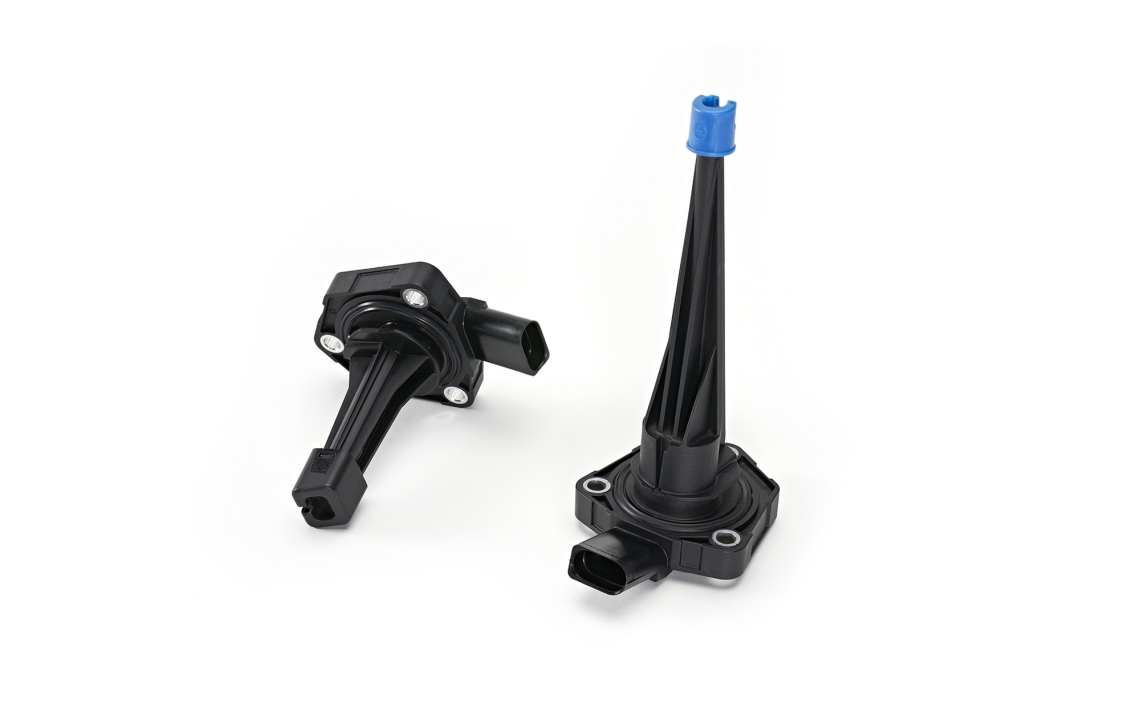
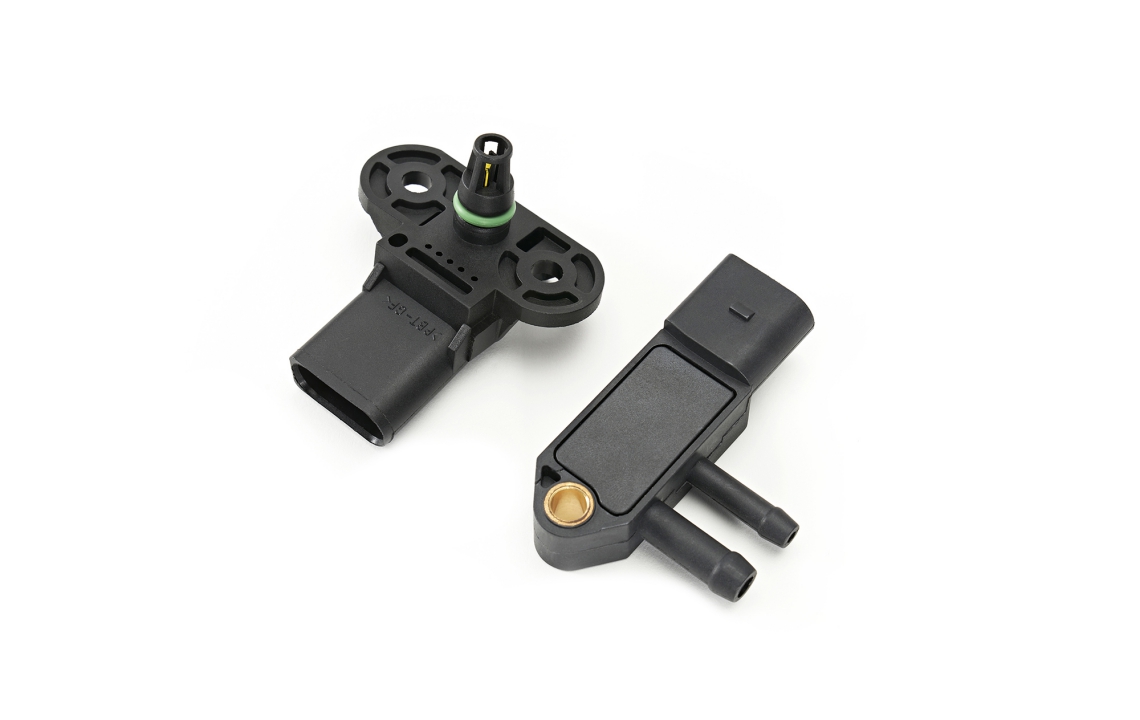
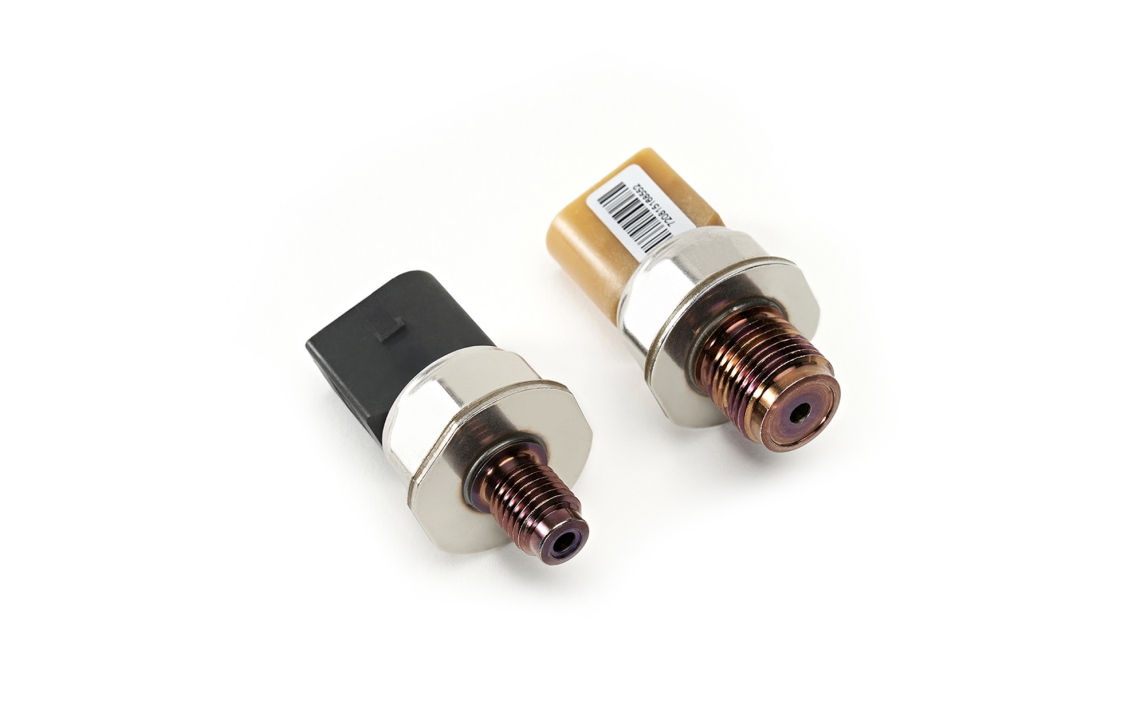
The crankshaft position sensor monitors as a multifunctional sensor used to set ignition timing, detect engine RPM and relative engine speed.
The camshaft position sensor is used to determine which cylinder is firing to synchronize the fuel injector and coil firing sequence.

 En
En